Obesity
Obesity


Back to top
HOW IS OBESITY CAUSED?
Energy imbalances, some genetic or hormonal conditions, and certain medicines are known to cause overweight or obesity.1b
Back to top
1. ENERGY IMBALANCE.
The fundamental cause of obesity is an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calories used.2a Energy is measured in calories. When you take in more calories than you use, this creates an energy imbalance causing your body to store fat. This means your energy IN (food/drinks) does not equal your energy OUT (exercise).1c,d
Back to top
HOW DOES YOUR BODY STORE ENERGY?

The amount of energy that your body gets from the food that you eat depends on:1f
- the TYPE of foods you eat
- how the food is PREPARED
- how LONG it has been since you last ate
Back to top
2. MEDICAL CONDITIONS THAT CAN CAUSE OBESITY
The body produces hormones that help maintain energy balances in the body. Conditions that affect these hormones can cause obesity.1g These include: Hypothyroidism. This condition is when a person has low levels of thyroid hormones. These low levels are associated with decreased metabolism and weight gain even when food intake is reduced. People with hypothyroidism also produce less body heat, have a lower body temperature and do not efficiently use stored fat for energy.1h Cushing’s syndrome. People with this condition have high levels of a hormone called cortisol. High cortisol levels make the body feel like it is under chronic stress. As a result, these people have an increase in appetite and the body stores more fat.1i Tumours. Some tumours near parts of the brain that control hunger can cause severe obesity.1j
Back to top
3. MEDICINES THAT CAN CAUSE OBESITY
There are also medicines that can cause weight gain that leads to overweight and obesity, such as antipsychotics, antidepressants, antiepileptic drugs, and medicines used for diabetes.1k Talk to your doctor if you notice weight gain while you are using any one of these or other medicines. Do not stop taking the medicines without consulting your doctor first.1k
Back to top
WHAT OTHER FACTORS INCREASE THE RISK OF BECOMING OBESE?
Unhealthy lifestyle habits put people at higher risk of being overweight or obese. These include lack of physical activity, unhealthy eating patterns, not enough sleep and high amounts of stress.1l Unhealthy environments. Factors such as easy access to unhealthy fast foods, limited access to safe areas to exercise and play and exposure to chemicals can increase the risk for overweight and obesity.1m Age. The risk of unhealthy weight gain increases as you get older, however childhood obesity is also a serious problem.1n Race and Sex. Overweight and obesity can differ between race and between males and females. The body stores fat differently in men compared to women. Women tend to store less unhealthy fat in the stomach area than men do; and women with polycystic ovary syndrome (a condition that reduces fertility) are at greater risk for obesity.1o,p Genetics. Obesity can run in families – this means that genes associated with obesity/weight gain can be passed down in your DNA to your child. Eating too much or too little during pregnancy can affect how your child stores and uses fat later in life. Studies have also shown that obese fathers have DNA changes in their sperm that can be passed on to their children.1q
Back to top
WHY IS OBESITY A WORLDWIDE PROBLEM?
Did you know?
Worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975!2b
As of 2016; almost 40 % of adults are overweight and 13 % are obese.2c
Obesity kills more people than underweight.2c
Obesity is preventable.2d
Globally there has been:2e
- an increased intake of energy-dense foods that are high in fat and sugars.
- an increase in physical inactivity due to the inactive nature of many jobs (desk-bound), changing modes of transportation (less walking) and increasing urbanisation.
Back to top
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
The signs of obesity include a high body mass index (BMI) and an unhealthy body fat distribution.1r
Back to top
BMI CALCULATION
BMI is a simple calculation that uses both weight and height to determine your weight category (see table below).2f A person with a BMI greater than or equal to 30 is classified as obese.2g,3
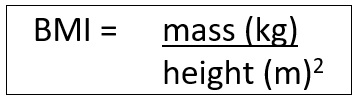
Back to top
TABLE: WEIGHT CATEGORIES
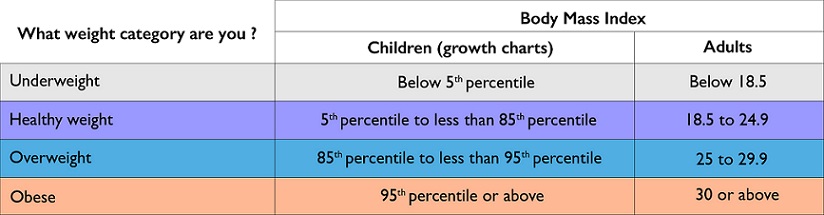
Unhealthy fat distribution – obesity is not only about having a high BMI. A waist circumference over 89 cm for women or 102 cm for men – can help diagnose obesity.3b Having an increased waist circumference suggests that you have increased amounts of fat in your abdomen (stomach area). This is a sign of obesity and increases your chances for obesity-related complications.1s-u
Back to top
WHAT ARE THE COMMON CONSEQUENCES/COMPLICATIONS OF BEING OBESE?
Obesity may cause the following complications:1v
- metabolic syndrome
- diabetes
- high cholesterol
- cardiovascular diseases (heart disease and stroke)
- breathing problems (sleep apnoea, asthma)
- back pain
- Osteoarthritis (a major cause of knee replacement surgery in patients who are obese for a long time)
- incontinence (weak bladder)
- low self-esteem or depression
- cancer
Almost half a million new cancer cases per year can be attributed to overweight and obesity!3c
Back to top
MANAGING OBESITY
Treatment depends on the cause and how severe the condition is. Treatments include lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating and increased physical activity (exercise). There are also weight-loss medicines that can be prescribed, and surgery may be a treatment option.1,4
Back to top
HOW CAN OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY BE REDUCED?
Following a healthy eating plan with fewer calories taken in is usually the first step in trying to treat overweight and obesity.4b When combined with healthy eating, regular physical activity will help you lose weight and stay at a healthy weight.4c
Back to top
WAYS IN WHICH YOU CAN CHANGE YOUR LIFESTYLE AND DECREASE YOUR RISK OF OBESITY:
Change to healthy eating patterns:1z,2h
- eat according to your daily calorie needs and not more!
- eat less saturated and trans fats
- avoid foods with added sugars
- increase consumption of fruit, vegetables, legumes, whole grains and nuts
- exercise more
- reduce screen time
- lack of sleep can affect hormones that control hunger urges
- stress can affect the brain and trigger the production of cortisol, a hormone that controls our energy balances and hunger urges
Government policies such as ‘sugar-tax’ on sweetened beverages are a way to help people make healthier dietary choices.2i,5a
Back to top
WHAT IS THE BIG DEAL WITH SOFT DRINKS?
Sugary drinks have no nutritional value. The average 500 ml fizzy drink contains around 10 spoons of sugar!5b Added sugar may be the unhealthiest ingredient in the modern diet6a
Medical References

October 20, 2021
Content Disclaimer:
You understand and acknowledge that all users of the Dis-Chem website or app are responsible for their own medical care, treatment, and oversight. All of the content provided on the website, are for INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY and DOES NOT CONSTITUTE THE PROVIDING OF MEDICAL ADVICE and is not intended to be a substitute for independent professional medical judgment, advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The content is not intended to establish a standard of care to be followed by a user of the website. You understand and acknowledge that you should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions or concerns you may have regarding your health. You also understand and acknowledge that you should never disregard or delay seeking medical advice relating to treatment or standard of care because of information contained in or transmitted through the website. Medical information changes constantly. Therefore the information on this website or on the linked websites should not be considered current, complete or exhaustive, nor should you rely on such information to recommend a course of treatment for you or any other individual. Reliance on any information provided on this website or any linked websites is solely at your own risk.









